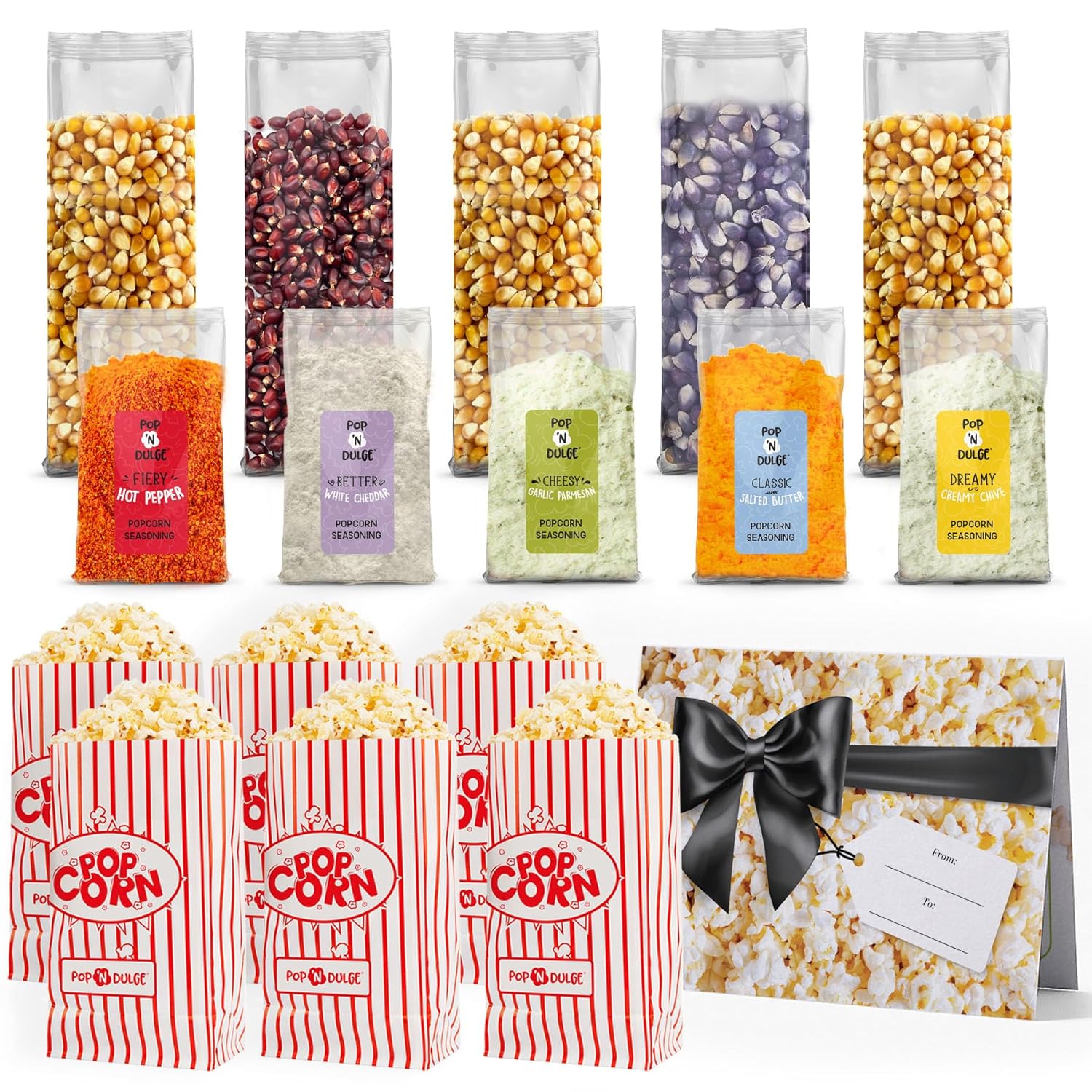
Popcorn Movie Night Supplies Popcorn Kernels Popcorn Seasoning 16 Pack, 5 Gourmet Popcorn Kernels, 5 Popcorn Seasoning Variety Packs Non-GMO Snacks, Includes 6 Bags, Gift Basket Idea









Price: [price_with_discount]
(as of [price_update_date] – Details)
From the brand




Ready for a cozy movie night?
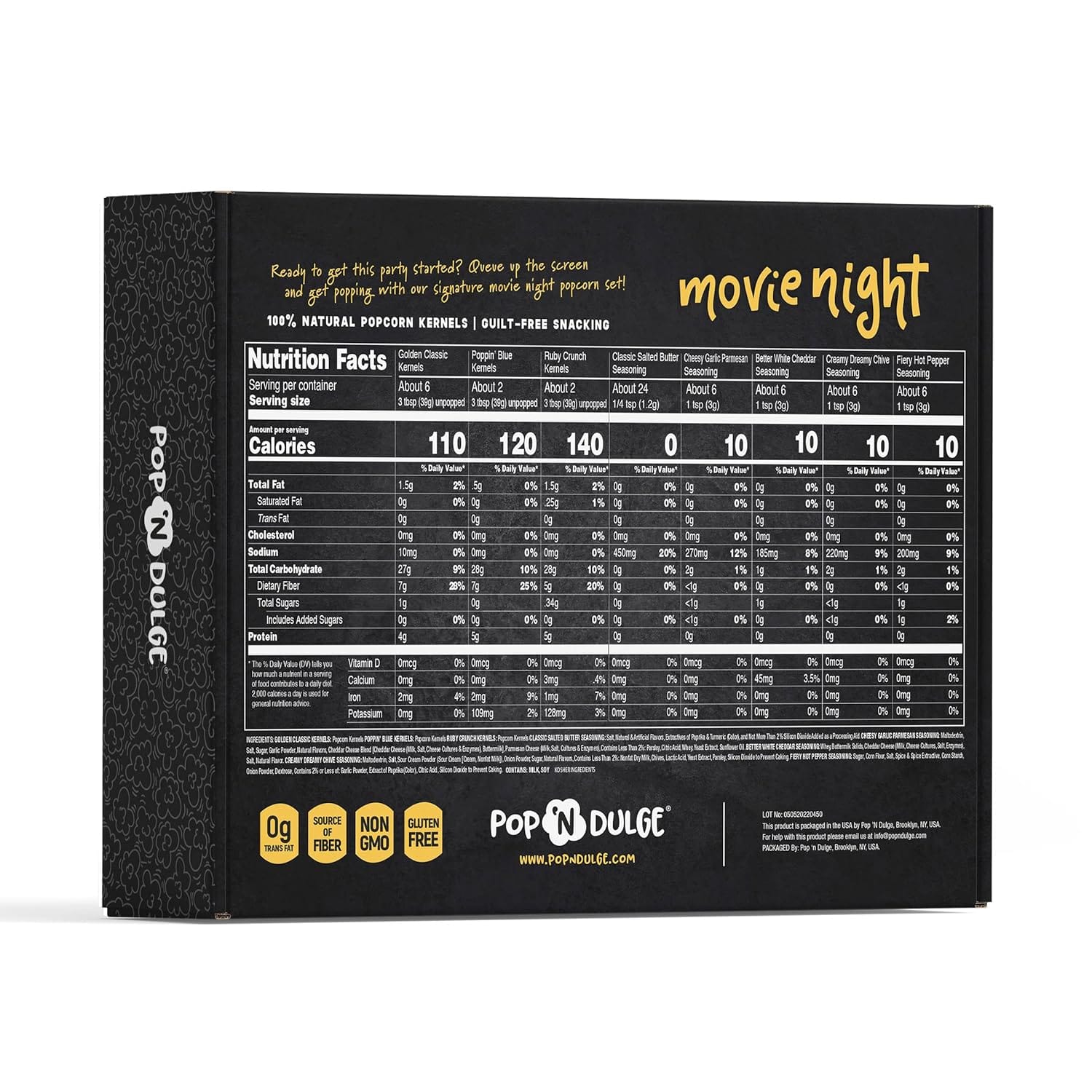
Ready to get this party started? Queue up the screen and get popping with our signature movie night popcorn set!
Make Movie Night Pop!


Making movie magic!
It just takes a little imagination to recreate the romance of your favorite theater at home.
Let’s Get Poppin’!


Your Health Matters: At Pop ‘N Dulge, our goal is to make flavors that pop, but without extra additives. That’s why we work with a registered dietitian to develop seasonings using natural ingredients – no food coloring allowed. Plus, all of our kernels and spices are naturally gluten free, non-GMO, and free from trans fats, and our kernels are sourced from farms in the USA.
Package Dimensions : 10.59 x 7.2 x 2.17 inches; 1.37 Pounds
Manufacturer : Pop ‘N Dulge
ASIN : B0B4X5SLKC
MOVIE NIGHT GIFT POPCORN KIT: It just takes a little imagination (and some delicious popcorn!) to recreate the magic of your favorite theater at home. Get the whole family on board or invite over your best buddies to pop some delicious movie popcorn for movie night. Make your favorite flavors, mix and match, and get creative with the best of all foodie gifts.
5 DELICIOUS POPCORN FLAVORS: Make movie magic with 5 mouth-watering, savory popcorn seasonings: Classic Salted Butter, Cheesy Garlic Parmesan, Better White Cheddar, Creamy Dreamy Chive, and Fiery Hot Pepper. Our Movie Night Popcorn Kit shows you how to whip up an exciting cinematic snack in no time. This popcorn seasoning variety pack is the perfect gift set for every occasion. It will make a great fathers day gifts and best gifts for dad.
PACKED WITH FUN: Add to the action on movie night with this delicious and festive popcorn gift set. Enjoy gourmet kernels in three different, natural earth tones: Golden Classic, Poppin’ Blue, and Ruby Crunch. Our Movie Night Popcorn Kit is sourced with the highest quality ingredients in mind. Whether you’re looking for memorable gifts for men who have everything or the best food gifts for women, there’s something for everyone in this tasty popcorn variety pack.
A GREAT GIFT: Date night, family gifts, foodie gifts, birthday gift ideas — there are so many occasions to enjoy our Pop ‘n Dulge Movie Night Popcorn Kit. Gourmet snacks like these popcorn kernels and savory popcorn seasonings are a great way to transform an ordinary evening into something special.
ALL NATURAL, NON-GMO KERNELS: We care about the quality of our products, because your health matters. That’s why a whole lot of effort goes into ensuring that our food kits contain only the best ingredients and products out there. All our kernels and spices are OU Kosher Certified, naturally gluten free, non-GMO, free from trans fats, and sourced from farms in the USA. Get ready for guilt-free snacking!
Customers say
Customers enjoy the variety of flavors and seasonings in the popcorn gift set. They find it a nice gift for popcorn lovers and like the attractive packaging. The quality is good and most kernels pop well. However, some customers feel the cost is not worth it and have issues with the pop rate. There are mixed opinions on the overall popcorn quality and size.
AI-generated from the text of customer reviews
Price: [price_with_discount]
(as of [price_update_date] – Details)


